NJU ICS PA 一些笔记
Do you know
本人代码水平拙劣🥲,实现部分仅供参考
南京大学 计算机科学与技术系 计算机系统基础 课程实验 2024
PA1 - 开天辟地的篇章
RTFSC
文件:nemu/src/monitor/sdb/sdb.c
原因:退出时 nemu_state.state 不是 “正常” 的
解决办法:
static int cmd_q(char *args) {
nemu_state.state = NEMU_QUIT;
return -1;
}监视点
基本框架
添加 w <expr> 和 d <index> 命令,来添加和删除监视点。
并且需要实现监视点池中链表的维护,监视点表达式的计算。
为了提高 NEMU 的性能,提供监视点功能的开关选项。
链表维护
监视点池中涉及监视点链表和空闲链表,通过 init_wp_pool() 来对其初始化。
void init_wp_pool() {
int i;
for (i = 0; i < NR_WP; i ++) {
wp_pool[i].NO = i;
wp_pool[i].next = (i == NR_WP - 1 ? NULL : &wp_pool[i + 1]);
}
head = NULL;
free_ = wp_pool;
}接着,通过 new_wp() 和 free_wp() 实现监视点的管理
int new_wp(char* args){
WP *p=NULL,*q=NULL;
if (free_==NULL)
{
printf("Watchpoints Limit");
return -1;
}
p=free_;
bool success=1;
p->result = expr(args,&success);
if (!success)return -1;
p->expr = strdup(args);
free_=free_->next;
if (head!=NULL)
{
q=head;
while (q->next!=NULL)q=q->next;
q->next=p;
return 1;
}
head=p;
head->next=NULL;
return 1;
}void free_wp(int no)
{
if (head==NULL)
{
printf("Watchpoint %d not found.\n",no);
return;
}
if (head->NO==no)
{
WP *wp=head;
head=wp->next;
wp->next=free_;
free_=wp;
return;
}
WP *p=NULL;
if (head!=NULL)
{
p=head;
while (1){
if (p->next->NO==no){
WP *wp=p->next;
p->next=wp->next;
wp->next=free_;
free_=wp;
return;
}
if (p->next==NULL)
{
printf("Watchpoint %d not found.\n",no);
return;
}
p=p->next;
}
}
}监视点求值
为了判断监视点的值是否发生变化,还需要在结构体中添加一个成员来记录。然后通过 check_expr() 来求值和判断变化。
bool check_expr(){
bool changed=false;
if (head==NULL)return 0;
WP *p;
bool success=true;
p=head;
word_t result = expr(p->expr,&success);
if (result!=p->result && success)
{
printf("Watchpoint %d changed at 0x%x.\n",p->NO,cpu.pc);
changed=true;
}
if (changed)return 1;
return 0;
}如何阅读手册
程序是个状态机
对于计算 1+2+...+100 的程序的状态机,它是确定性的。
(0, x, x) -> (1, 0, x) -> (2, 0, 0) -> (3, 0, 1) -> (4, 1, 1) -> (5, 1, 2) -> (6, 3, 2) -> ... -> (199,4851, 99) -> (200, 4950, 99) -> (201, 4950, 100) -> (202, 5050, 100)理解基础设施
不必多说,使用过调试器的话肯定有所体会。
RTFM
riscv32 有哪几种指令格式?
There are four core instruction formats.
Register-Type, Immediate-Type, Store-Type, Upper Immediate-Type.
LUI 指令的行为是什么?
LUI (load upper immediate) is used to build 32-bit constants and uses the U-type format. LUI places the 32-bit U-immediate value into the destination register rd, filling in the lowest 12 bits with zeros.
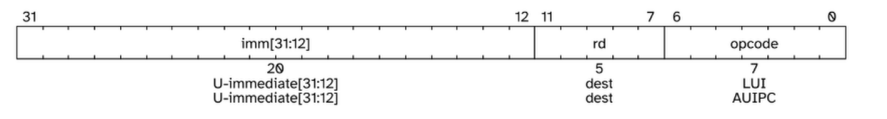
mstatus 寄存器的结构是怎么样的?
The mstatus (Machine Status) register is an MXLEN-bit read/write
register formatted as shown in figures below. It's a Control and
Status Register.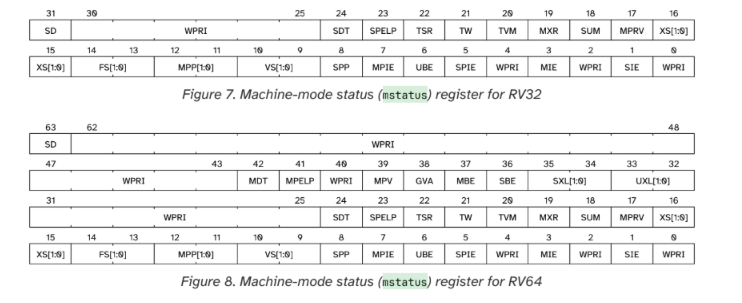
为什么要使用 -Wall 和 -Werror?
At section 3.9, we found that:
-Werror Turn all warnings into errors.
-Wall This enables all the warnings about constructions
that some users consider questionable, and that are easy to avoid (or
modify to prevent the warning), even in conjunction with macros. This
also enables some language-specific warnings.
To add these options, we can leverage compilers to identify potential issues in our programs.
shell 命令
使用 find . -type f \( -name "*.c" -o -name "*.h" \) -print0 | xargs -0 wc -l 来统计行数
由于我环境经历了多次迁移,似乎把 git 弄坏了(
不过毕竟我没有提交作业的需求,就不注意这些细节了
PA2 - 简单复杂的机器
不停计算的机器
画出在 YEMU 上执行的加法程序的状态机
类似地,使用一个 6 元组来分别表示 PC, R [0], R [1], M [x], M [y], M [z].
(0, 0, 0, x, y ,0) -> (1, y, 0, x, y, 0) -> (2, y, y, x, y, 0) -> (3, x, y , x, y, 0) -> (4, x+y, y, x, y, 0) -> (5, x+y, y, x, y, x+y)RTFSC(2)
立即数背后的故事
1. 假设我们需要将 NEMU 运行在 Motorola 68k 的机器上 (把 NEMU 的源代码编译成 Motorola 68k 的机器码)
此时读取的字节序列会被解释为大端序的,如果在二进制文件中以小端序存储,可能会导致问题。
2. 假设我们需要把 Motorola 68k 作为一个新的 ISA 加入到 NEMU 中
我们需要正确模拟大端序对应的存储结构与解释方式。
立即数背后的故事 (2)
在 RISC-V32 中,一般使用分部加载的方式:
通过 lui 加载高 20 位,addi 加载低 12 位
lui x10, 0x0D000
addi x10, x10, 0x721auipc 的执行过程
QEMU 内建的第一条指令,正是 auipc
0x00000297, // auipc t0,0在 QEMU 运行过程中,首先调用 exec_once() 来进入相应的处理流程。
static void exec_once(Decode *s, vaddr_t pc) {
s->pc = pc;
s->snpc = pc;
isa_exec_once(s);
cpu.pc = s->dnpc;
//some macros...
}传入的 Decode 是一个包含与 PC 有关变量的结构体
typedef struct Decode {
vaddr_t pc;
vaddr_t snpc; // static next pc
vaddr_t dnpc; // dynamic next pc
ISADecodeInfo isa;
IFDEF(CONFIG_ITRACE, char logbuf[128]);
} Decode;然后调用 isa_exec_once(s),对于不同的架构,具体的定义不同。
instruction fetch
在 risc-v32 的实现中,代码如下
int isa_exec_once(Decode *s) {
s->isa.inst = inst_fetch(&s->snpc, 4);
return decode_exec(s);
}具体的过程又涉及到 vaddr_read() 和 paddr_read(),处理 mmio 地址和 pmem 地址,物理内存上使用 host_read() 读取主机内存上的不同长度字节。
instruction decode
完成取指调用的一系列函数后,isa_exec_once() 会返回 decode_exec(s)
将指令与相应的模式匹配
static int decode_exec(Decode *s) {
s->dnpc = s->snpc;
INSTPAT_START();
INSTPAT("??????? ????? ????? ??? ????? 00101 11", auipc , U, R(rd) = s->pc + imm);
INSTPAT("??????? ????? ????? 100 ????? 00000 11", lbu , I, R(rd) = Mr(src1 + imm, 1));
INSTPAT("??????? ????? ????? 000 ????? 01000 11", sb , S, Mw(src1 + imm, 1, src2));
INSTPAT("0000000 00001 00000 000 00000 11100 11", ebreak , N, NEMUTRAP(s->pc, R(10))); // R(10) is $a0
INSTPAT("??????? ????? ????? ??? ????? ????? ??", inv , N, INV(s->pc));
INSTPAT_END();
R(0) = 0; // reset $zero to 0
return 0;
}其中,auipc 对应的 (U-Type) 格式如下:

execute
QEMU 在宏中定义了 auipc 的具体行为:
INSTPAT("??????? ????? ????? ??? ????? 00101 11", auipc , U, R(rd) = s->pc + imm);pattern_decode()中的宏处理了格式字符串:
static inline void pattern_decode(const char *str, int len,
uint64_t *key, uint64_t *mask, uint64_t *shift) {
uint64_t __key = 0, __mask = 0, __shift = 0;
macro64(0);//宏展开,遍历了6位二进制数0b000000的任意取值
panic("pattern too long");
finish:
*key = __key >> __shift;
*mask = __mask >> __shift;
*shift = __shift;
}运行第一个 C 程序
我们需要在此部分实现的指令有 lui, addi,
jal, jalr.
按照 RISC-V 手册实现即可。
需要注意不同指令对待操作数的符号和截断处理。
指令名对照
方法很多,可以根据 opcode 段查询。
程序,运行时环境与 AM
运行时环境
要求实现 spirntf() 等等库函数,可以参考 glibc 或者 STFW.
RTFSC(3)
对各个 section 的定义如下
//abstract-machine/scripts/linker.ld
ENTRY(_start)
PHDRS { text PT_LOAD; data PT_LOAD; }
SECTIONS {
/* _pmem_start and _entry_offset are defined in LDFLAGS */
. = _pmem_start + _entry_offset;
.text : {
*(entry)
*(.text*)
} : text
etext = .;
_etext = .;
.rodata : {
*(.rodata*)
}
.data : {
*(.data)
} : data
edata = .;
_data = .;
.bss : {
_bss_start = .;
*(.bss*)
*(.sbss*)
*(.scommon)
}
_stack_top = ALIGN(0x1000);
. = _stack_top + 0x8000;
_stack_pointer = .;
end = .;
_end = .;
_heap_start = ALIGN(0x1000);
}阅读 Makefile
Check environment and arguments:
### Override checks when `make clean/clean-all/html`
ifeq ($(findstring $(MAKECMDGOALS),clean|clean-all|html),)
### Print build info message
$(info # Building $(NAME)-$(MAKECMDGOALS) [$(ARCH)])
//...
### Check: environment variable `$ARCH` must be in the supported list
ARCHS = $(basename $(notdir $(shell ls $(AM_HOME)/scripts/*.mk)))
ifeq ($(filter $(ARCHS), $(ARCH)), )
$(error Expected $$ARCH in {$(ARCHS)}, Got "$(ARCH)")
endif
### Checks end here
endifInclude AM makefile specified by $(ARCH):
-include $(AM_HOME)/scripts/$(ARCH).mk in $(ARCH).mk,
it includes nemu.mk, which builds NEMU related driver
and runs NEMU.
it also includes another arch related .mk that overwrites
ARCH_H.
include $(AM_HOME)/scripts/isa/riscv.mk
include $(AM_HOME)/scripts/platform/nemu.mk
CFLAGS += -DISA_H=\"riscv/riscv.h\"
AM_SRCS += riscv/nemu/start.S \
riscv/nemu/cte.c \
riscv/nemu/trap.S \
riscv/nemu/vme.cDefine compilation rule:
## 5. Compilation Rules
### Rule (compile): a single `.c` -> `.o` (gcc)
$(DST_DIR)/%.o: %.c
@mkdir -p $(dir $@) && echo + CC $<
@$(CC) -std=gnu11 $(CFLAGS) -c -o $@ $(realpath $<)
### Rule (compile): a single `.cc` -> `.o` (g++)
$(DST_DIR)/%.o: %.cc
@mkdir -p $(dir $@) && echo + CXX $<
@$(CXX) -std=c++17 $(CXXFLAGS) -c -o $@ $(realpath $<)
### Rule (compile): a single `.cpp` -> `.o` (g++)
$(DST_DIR)/%.o: %.cpp
@mkdir -p $(dir $@) && echo + CXX $<
@$(CXX) -std=c++17 $(CXXFLAGS) -c -o $@ $(realpath $<)
### Rule (compile): a single `.S` -> `.o` (gcc, which preprocesses and calls as)
$(DST_DIR)/%.o: %.S
@mkdir -p $(dir $@) && echo + AS $<
@$(AS) $(ASFLAGS) -c -o $@ $(realpath $<)
### Rule (recursive make): build a dependent library (am, klib, ...)
$(LIBS): %:
@$(MAKE) -s -C $(AM_HOME)/$* archive
### Rule (link): objects (`*.o`) and libraries (`*.a`) -> `IMAGE.elf`, the final ELF binary to be packed into image (ld)
$(IMAGE).elf: $(LINKAGE) $(LDSCRIPTS)
@echo \# Creating image [$(ARCH)]
@echo + LD "->" $(IMAGE_REL).elf
ifneq ($(filter $(ARCH),native),)
@$(CXX) -o $@ -Wl,--whole-archive $(LINKAGE) -Wl,-no-whole-archive $(LDFLAGS_CXX)
else
@$(LD) $(LDFLAGS) -o $@ --start-group $(LINKAGE) --end-group
endif
### Rule (archive): objects (`*.o`) -> `ARCHIVE.a` (ar)
$(ARCHIVE): $(OBJS)
@echo + AR "->" $(shell realpath $@ --relative-to .)
@$(AR) rcs $@ $^
### Rule (`#include` dependencies): paste in `.d` files generated by gcc on `-MMD`
-include $(addprefix $(DST_DIR)/, $(addsuffix .d, $(basename $(SRCS))))Build the project in order below
image: image-dep
archive: $(ARCHIVE)
image-dep: $(LIBS) $(IMAGE).elf
.NOTPARALLEL: image-dep
Building add-run [riscv64-nemu]
Building am-archive [riscv64-nemu]
Building klib-archive [riscv64-nemu]
+ CC tests/add.c
Creating image [riscv64-nemu]
+ LD -> build/add-riscv64-nemu.elf
+ OBJCOPY -> build/add-riscv64-nemu.bin实现常用的库函数
stdarg 是如何实现的?
在
参考 GNU/gcc-15.2.0 中 i386 的实现:
计算固定参数的大小
//gcc-15.2.0/gcc/config/i386/i386.cc
/* Count number of gp and fp argument registers used. */
words = crtl->args.info.words;
n_gpr = crtl->args.info.regno;
n_fpr = crtl->args.info.sse_regno;
if (cfun->va_list_gpr_size)
{
type = TREE_TYPE (gpr);
t = build2 (MODIFY_EXPR, type,
gpr, build_int_cst (type, n_gpr * 8));
TREE_SIDE_EFFECTS (t) = 1;
expand_expr (t, const0_rtx, VOIDmode, EXPAND_NORMAL);
}
if (TARGET_SSE && cfun->va_list_fpr_size)
{
type = TREE_TYPE (fpr);
t = build2 (MODIFY_EXPR, type, fpr,
build_int_cst (type, n_fpr * 16 + 8*X86_64_REGPARM_MAX));
TREE_SIDE_EFFECTS (t) = 1;
expand_expr (t, const0_rtx, VOIDmode, EXPAND_NORMAL);
}处理栈上的 overflow area, register save area.
/* Find the overflow area. */
type = TREE_TYPE (ovf);
if (cfun->machine->split_stack_varargs_pointer == NULL_RTX)
ovf_rtx = crtl->args.internal_arg_pointer;
else
ovf_rtx = cfun->machine->split_stack_varargs_pointer;
t = make_tree (type, ovf_rtx);
if (words != 0)
t = fold_build_pointer_plus_hwi (t, words * UNITS_PER_WORD);
t = build2 (MODIFY_EXPR, type, ovf, t);
TREE_SIDE_EFFECTS (t) = 1;
expand_expr (t, const0_rtx, VOIDmode, EXPAND_NORMAL);
if (ix86_varargs_gpr_size || ix86_varargs_fpr_size)
{
/* Find the register save area.
Prologue of the function save it right above stack frame. */
type = TREE_TYPE (sav);
t = make_tree (type, frame_pointer_rtx);
if (!ix86_varargs_gpr_size)
t = fold_build_pointer_plus_hwi (t, -8 * X86_64_REGPARM_MAX);
t = build2 (MODIFY_EXPR, type, sav, t);
TREE_SIDE_EFFECTS (t) = 1;
expand_expr (t, const0_rtx, VOIDmode, EXPAND_NORMAL);
}基础设施 (2)
指令环形缓冲区 - iringbuf
实现一个环形缓冲区,每次执行指令时写入即可
typedef struct
{
char buf[10][128];
int head;
int tail;
} LogRingbuf;
IFDEF(CONFIG_ITRACE, LogRingbuf ringbuf);
void ringbuf_push(LogRingbuf *r, const char* log) {
strcpy(r->buf[r->head], log);
r->head = (r->head+1) % 10;
if(r->head == r->tail) r->tail = (r->tail+1) % 10;
}
void ringbuf_puts(LogRingbuf *r) {
for(int i = r->tail; i!=r->head; i = (i+1)%10) {
printf("%s\n", r->buf[i]);
}
}函数调用的踪迹 - ftrace
偷懒了,并没有完全实现(
先读取传入的 ELF:
void init_ftrace(const char* elf) {
Elf64_Ehdr elf_header;
FILE *fp = fopen(elf, "rb");
if (fp == NULL) {
printf("Failed to open file %s\n", elf);
return;
}
size_t count = fread(&elf_header, 1, sizeof(Elf64_Ehdr), fp);
assert(count == sizeof(Elf64_Ehdr));
parse_symbols(fp, &elf_header);
}根据 ELF 的结构,我们先读取 Elf64_Ehdr:
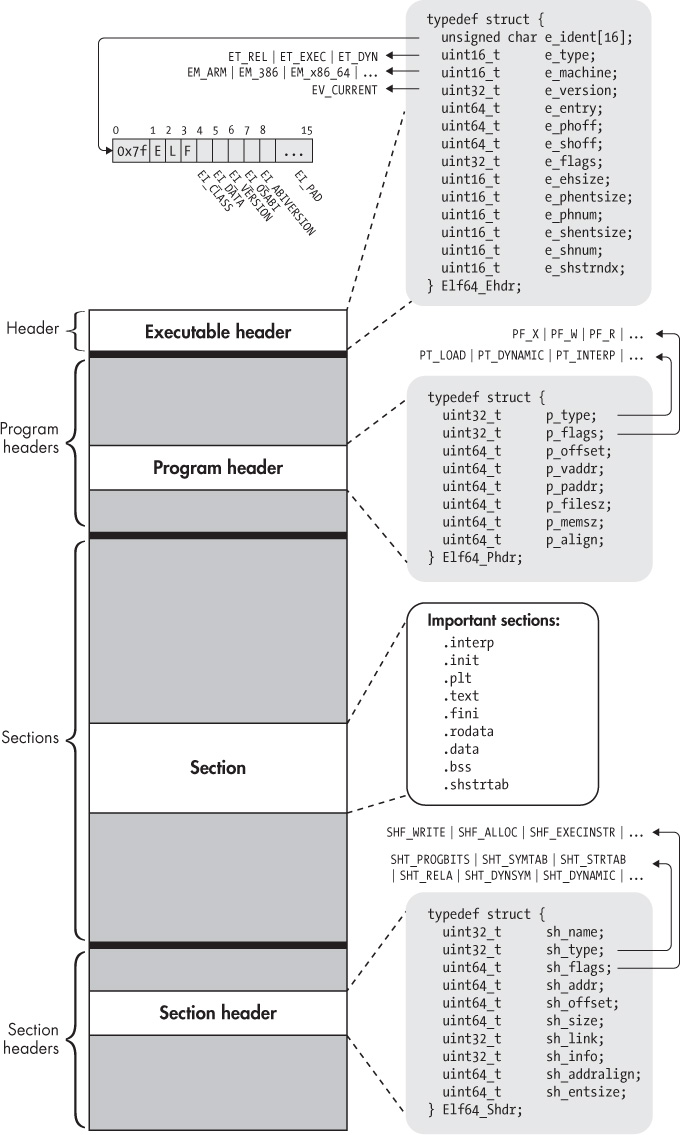
ELF header (Ehdr)
The ELF header is described by the type Elf32_Ehdr or Elf64_Ehdr:
#define EI_NIDENT 16
typedef struct {
unsigned char e_ident[EI_NIDENT];
uint16_t e_type;
uint16_t e_machine;
uint32_t e_version;
ElfN_Addr e_entry;
ElfN_Off e_phoff;
ElfN_Off e_shoff;
uint32_t e_flags;
uint16_t e_ehsize;
uint16_t e_phentsize;
uint16_t e_phnum;
uint16_t e_shentsize;
uint16_t e_shnum;
uint16_t e_shstrndx;
} ElfN_Ehdr;解析具体的符号表,并维护一个单向链表:
void parse_symbols(FILE *fp, Elf64_Ehdr *elf_header) {
Elf64_Shdr *sh_table = malloc(elf_header->e_shnum * sizeof(Elf64_Shdr));
fseek(fp, elf_header->e_shoff, SEEK_SET);
size_t ret = fread(sh_table, sizeof(Elf64_Shdr), elf_header->e_shnum, fp);
assert(ret == elf_header->e_shnum);
Elf64_Shdr *symtab_shdr = NULL;
Elf64_Shdr *strtab_shdr = NULL;
for (int i = 0; i < elf_header->e_shnum; i++) {
if (sh_table[i].sh_type == SHT_SYMTAB) {
symtab_shdr = &sh_table[i];
if (symtab_shdr->sh_link < elf_header->e_shnum) {
strtab_shdr = &sh_table[symtab_shdr->sh_link];
}
break;
}
}
if (!symtab_shdr || !strtab_shdr) {
printf("Symbol table or string table not found.\n");
free(sh_table);
return;
}
Elf64_Sym *sym_table = malloc(symtab_shdr->sh_size);
fseek(fp, symtab_shdr->sh_offset, SEEK_SET);
ret = fread(sym_table, symtab_shdr->sh_size, 1, fp);
assert(ret == 1);
char *strtab = malloc(strtab_shdr->sh_size);
fseek(fp, strtab_shdr->sh_offset, SEEK_SET);
ret = fread(strtab, strtab_shdr->sh_size, 1, fp);
assert(ret == 1);
int num_symbols = symtab_shdr->sh_size / sizeof(Elf64_Sym);
//printf("Parsing %d symbols...\n", num_symbols);
for (int i = 0; i < num_symbols; i++) {
const char *symbol_name = &strtab[sym_table[i].st_name];
Elf64_Addr symbol_addr = sym_table[i].st_value;
unsigned char symbol_type = ELF64_ST_TYPE(sym_table[i].st_info);
if (symbol_type == STT_FUNC) {
// printf("Found function: %s at address 0x%lx\n", symbol_name, symbol_addr);
ftrace_append(symbol_name, symbol_addr);
}
}
free(sh_table);
free(sym_table);
free(strtab);
}Section header 中存放了各个 section 的信息
Section header (Shdr)
A file's section header table lets one locate all the file's sections. The section header table is an array of Elf32_Shdr or Elf64_Shdr structures. The ELF
header's e_shoff member gives the byte offset from the beginning of the file to the section header table. e_shnum holds the number of entries the section
header table contains. e_shentsize holds the size in bytes of each entry.
A section header table index is a subscript into this array. Some section header table indices are reserved: the initial entry and the indices between
SHN_LORESERVE and SHN_HIRESERVE. The initial entry is used in ELF extensions for e_phnum, e_shnum, and e_shstrndx; in other cases, each field in the initial
entry is set to zero. An object file does not have sections for these special indices:
SHN_UNDEF
This value marks an undefined, missing, irrelevant, or otherwise meaningless section reference.
SHN_LORESERVE
This value specifies the lower bound of the range of reserved indices.
SHN_LOPROC
SHN_HIPROC
Values greater in the inclusive range [SHN_LOPROC, SHN_HIPROC] are reserved for processor-specific semantics.
SHN_ABS
This value specifies the absolute value for the corresponding reference. For example, a symbol defined relative to section number SHN_ABS has an ab‐
solute value and is not affected by relocation.
SHN_COMMON
Symbols defined relative to this section are common symbols, such as FORTRAN COMMON or unallocated C external variables.
SHN_HIRESERVE
This value specifies the upper bound of the range of reserved indices. The system reserves indices between SHN_LORESERVE and SHN_HIRESERVE, inclu‐
sive. The section header table does not contain entries for the reserved indices.
Elf64_Sym 的定义如下:
String and symbol tables
String table sections hold null-terminated character sequences, commonly called strings. The ob‐
ject file uses these strings to represent symbol and section names. One references a string as
an index into the string table section. The first byte, which is index zero, is defined to hold
a null byte ('\0'). Similarly, a string table's last byte is defined to hold a null byte, ensur‐
ing null termination for all strings.
An object file's symbol table holds information needed to locate and relocate a program's sym‐
bolic definitions and references. A symbol table index is a subscript into this array.
typedef struct {
uint32_t st_name;
//This member holds an index into the object file's symbol string table, which holds character representations of the symbol names. If the value is nonzero, it represents a string table index that gives the symbol name. Otherwise, the symbol has no name.
unsigned char st_info;
unsigned char st_other;
uint16_t st_shndx;
Elf64_Addr st_value;
uint64_t st_size;
} Elf64_Sym;
后面遇到 jal 等跳转指令查找这个链表,计算偏移就可以了。
Differential Testing
框架已经实现好了相应的接口,实现一下比较寄存器的值
bool isa_difftest_checkregs(CPU_state *ref_r, vaddr_t pc) {
bool ok = true;
for(int i=0;i<32;i++) {
if(ref_r->gpr[i] != cpu.gpr[i]) {
printf("\n [difftest] inequal reg value in %s: 0x%lx\n", regs[i], ref_r->gpr[i]);
ok = false;
}
}
if(ref_r->pc != cpu.pc) {
printf("\n [difftest] inequal pc: 0x%lx\n",ref_r->pc);
ok = false;
}
return ok;
}输入输出
实现需要的 IOE 功能都比较简单,这里在跑 microbench 的时候遇到了一个比较怪的问题。
difftest 提示
References
- https://lf-riscv.atlassian.net/wiki/spaces/HOME/pages/16154769/RISC-V+Technical+Specifications#ISA-Specifications
- https://gcc.gnu.org/onlinedocs/gcc-15.1.0/gcc.pdf
- https://elixir.bootlin.com/glibc/glibc-2.42.9000/source
- https://gist.github.com/x0nu11byt3/bcb35c3de461e5fb66173071a2379779#file-elf_format_cheatsheet-md